Dam Safety Geophysical Services Provider in India
Back to ServicesDams in the country represent a major investment and huge benefits to population in terms of irrigation, power and flood control. Most of the big dams are very old and regular monitoring and maintenance of these dams is of utmost importance for continuing benefits. Unlike soil investigations, critical nature of dams, does not permit traditional invasive inspections by means of drilling, and such inspections are best avoided unless extremely important, and are done only when problem is too grave.
Geophysical techniques, by virtue of their non-invasive and non-destructive nature, offer an excellent solution for investigation or regular monitoring of dams, and detection of anomalous conditions which might snowball into major problems if left untreated.
Various geophysical methods are available to investigate the problems of earthen, masonry, concrete or composite dams:
- Leak path detection
- Internal Erosion
- Identification of zone of water accumulation
- Cavity/ sinkhole
- Concrete degradation
| GEOPHYSICAL METHODS | ISSUES AND CONCERNS | ||||||
| CONCRETE DAM | EARTH EMBANKMENT DAMS | MASONRY DAMS | |||||
| CRACKS | DEGRADATION | WATER LEAKS | LANDSLIDE | SINK HOLES | WATER LEAKS | STRENGTH | |
| Electrical Resistivity | |||||||
| Streaming Potential | |||||||
| Georadar | |||||||
| Radar Tomography | |||||||
| Seismic Tomography | |||||||
| Seismic Refraction | |||||||
| ReMi | |||||||
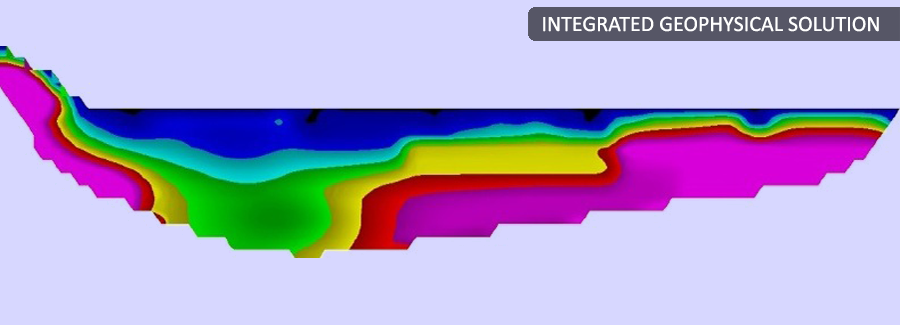
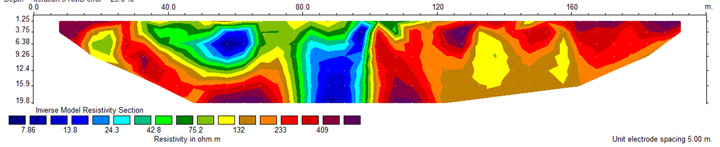
The results of electrical surveys carried out on the crest of a dam are presented as vertical sections showing the electrical properties of the dam materials. Electrical currents travel along preferential pathways in the most conductive materials such as dam core composed on fine grained materials. ERI for dam safety is paramount because the electrical resistivity imaging provides picture of internal resistivity distribution of the dam structure, identifying areas of water saturation in the dam body, and thus identifying the zones of water accumulation and wetting.
 Streaming Potential
Streaming Potential
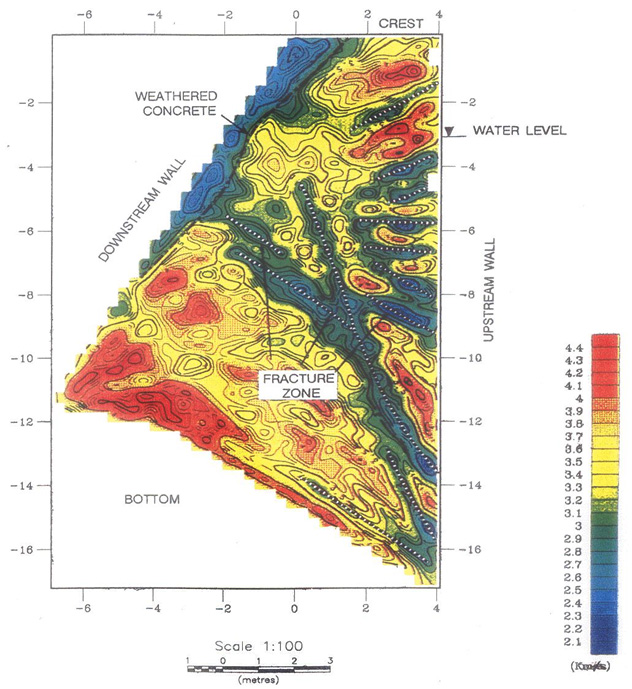
The streaming potential method consists of measuring the electrical potential by flowing water within a structure or subsurface. Common applications for SP measurements include assessing seepage from dams and embankments.
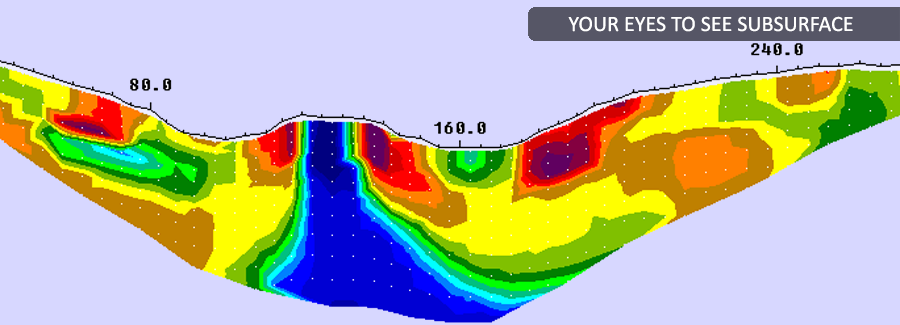
Ground Penetrating RadarGPR survey is conducted to identify shallow cracks, cavities and voids in the dam body. The survey also might reveal the stratigraphy in the dam body based on contrast in dielectric constant.
Seismic TomographyProvides detailed information on strength of material within the dam, based on seismic velocity.
 Seismic Refraction
Seismic Refraction
Can be used to determine bedrock topography and presence of fractures, faults and shear zones, if any.
ReMiTo determine shear wave velocities in Dam body.